Textbook Question
Balance the following equations. (c) NH4ClO4 + Al → Al2O3 + N2 + Cl2 + H2O
867
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


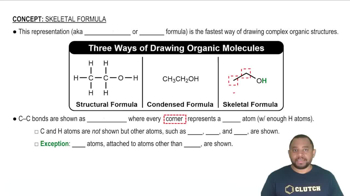
Balance the following equations. (c) NH4ClO4 + Al → Al2O3 + N2 + Cl2 + H2O
Balance the following equations. (a) CO(NH2)2(aq) + HOCl(aq) --> NCl3(aq) + CO2(aq) + H2O(l)
Balance the following equations. (b) Ca3(PO4)2(s) + SiO2(s) + C(s) --> P4(g) + CaSiO3(l) + CO(g)
What are the molecular (formula) weights of the following substances? (b) C4H8O2 (butyric acid, responsible for the odor of rancid butter)
What are the molecular (formula) weights of the following substances? (c) CF2Cl2 (a chlorofluorocarbon that destroys the stratospheric ozone layer