
Several processes are given in the table and labeled as endo- thermic or exothermic and given a sign for ∆H°. Which process is labeled with the correct sign of ∆H° and correct classification as endothermic or exothermic? (LO 9.8) Process (b) Methane, the main component of natural gas, is burned to produce a flame on a stovetop.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
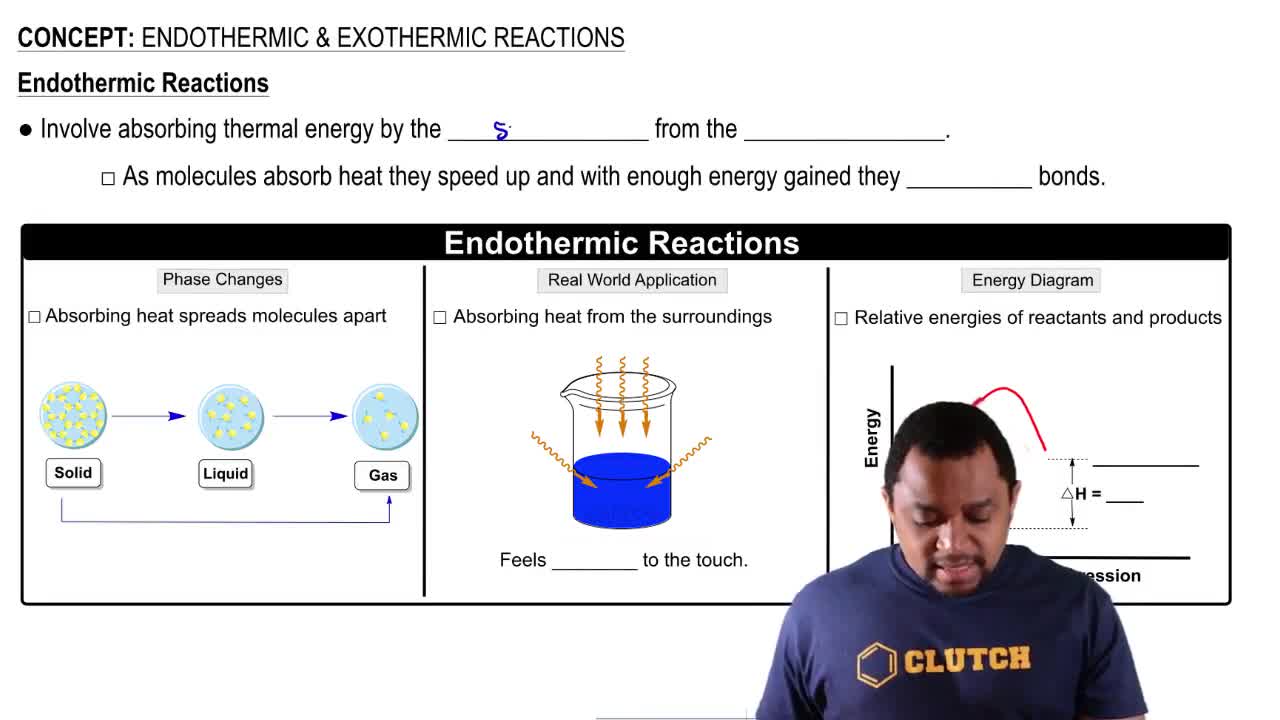
Enthalpy Change (∆H°)

Combustion of Methane

Several processes are given in the table and labeled as endo- thermic or exothermic and given a sign for ∆H°. Which process is labeled with the correct sign of ∆H° and correct classification as endothermic or exothermic? (LO 9.8) Process (a) Ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, and the temperature of the solution decreases.
Several processes are given in the table and labeled as endo- thermic or exothermic and given a sign for ∆H°. Which process is labeled with the correct sign of ∆H° and correct classification as endothermic or exothermic? (LO 9.8) Process (c) Water freezes into ice in the freezer.
Several processes are given in the table and labeled as endo- thermic or exothermic and given a sign for ∆H°. Which process is labeled with the correct sign of ∆H° and correct classification as endothermic or exothermic? (LO 9.8) Process (d) Rubbing alcohol evaporates from your skin.
