Textbook Question
How was it established experimentally that the frequency of recombination (crossing over) between two genes is related to the distance between them along the chromosome?
744
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


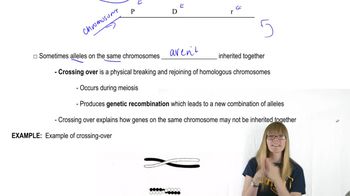
How was it established experimentally that the frequency of recombination (crossing over) between two genes is related to the distance between them along the chromosome?
How do we know that crossing over results from a physical exchange between chromatids?
How do we know that sister chromatids undergo recombination during mitosis?
When designed matings cannot be conducted in an organism (for example, in humans), how do we learn that genes are linked, and how do we map them?