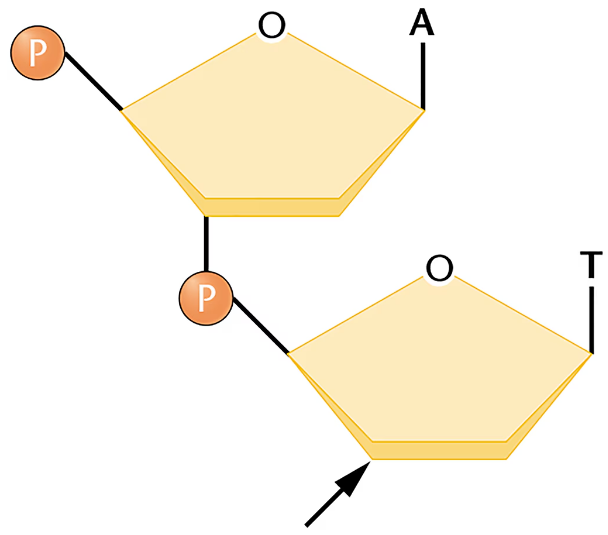
To gauge the fidelity of DNA synthesis, Arthur Kornberg and colleagues devised a technique called nearest-neighbor analysis, which determines the frequency with which any two bases occur adjacent to each other along the polynucleotide chain (J. Biol. Chem. 236: 864–875). This test relies on the enzyme spleen phosphodiesterase (see the previous problem). DNA is synthesized by polymerization of 5'-nucleotides—that is, each nucleotide is added with the phosphate on the deoxyribose. However, as shown in the accompanying figure, the phosphodiesterase enzyme cleaves DNA between the phosphate and the C-5' atom, thereby producing 3'-nucleotides. In this test, the phosphates on only one of the four nucleotide precursors of DNA (cytidylic acid, for example) are made radioactive with ³²P, and DNA is synthesized. Then the DNA is subjected to enzymatic cleavage, in which the radioactive phosphate is transferred to the base that is the 'nearest neighbor' on the 5' side of all cytidylic acid nucleotides.
Following four separate experiments, in each of which a different one of the four nucleotide types is radioactive, the frequency of all 16 possible nearest neighbors can be calculated. When Kornberg applied the nearest-neighbor frequency test to the DNA template and resultant product from a variety of experiments, he found general agreement between the nearest-neighbor frequencies of the two. Analysis of nearest-neighbor data led Kornberg to conclude that the two strands of the double helix are in opposite polarity to one another. Demonstrate this approach by determining the outcome of such an analysis if the strands of DNA shown here are (a) antiparallel versus (b) parallel: