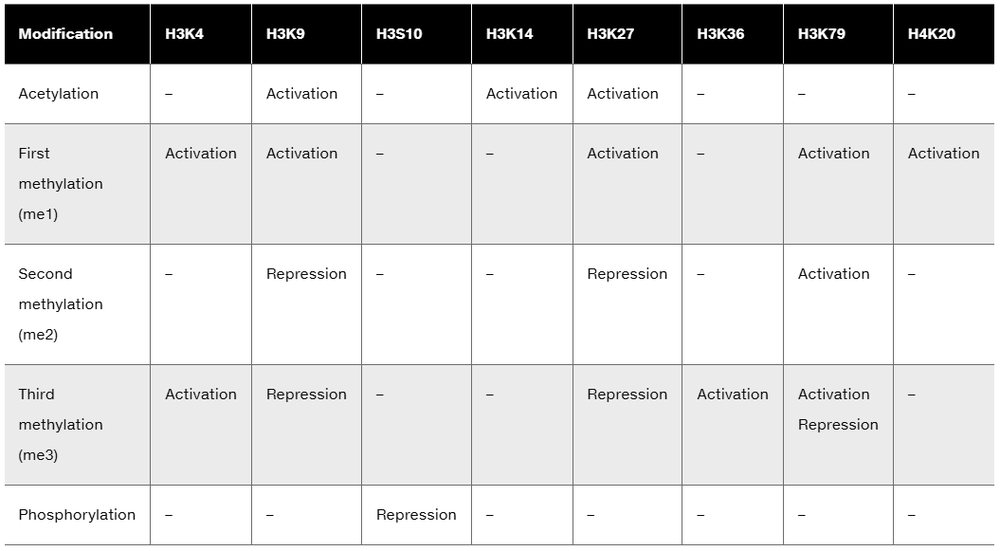
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder with a clinical profile of obesity, intellectual disability, and short stature. It can be caused in several ways. Most common is a deletion on the paternal copy of chromosome 15, but it can also be caused by an epigenetic imprinting disorder and uniparental disomy, an event in which the affected child receives two copies of the maternal chromosome 15. A child with PWS comes to your clinic for a diagnosis of the molecular basis for this condition. The gel below shows the results of testing with short tandem repeats (STRs) from the region of chromosome 15 associated with the disorder.
Based on your interpretation of the data, what is the cause of PWS in this case? Explain your reasoning.