What is functional genomics? How does it differ from comparative genomics?
Ch. 21 - Genomic Analysis

Chapter 21, Problem 6
Annotation involves identifying genes and gene-regulatory sequences in a genome. List and describe characteristics of a genome that are hallmarks for identifying genes in an unknown sequence. What characteristics would you look for in a bacterial genome? A eukaryotic genome?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that gene annotation involves recognizing specific features in DNA sequences that indicate the presence of genes or regulatory elements. These features differ between bacterial and eukaryotic genomes due to their structural and functional differences.
For a bacterial genome, look for characteristics such as: a) Open Reading Frames (ORFs) that are long stretches without stop codons, b) Promoter sequences like the -10 (Pribnow box) and -35 regions upstream of genes, c) Ribosome Binding Sites (Shine-Dalgarno sequences) near the start codon, d) Operon structures where multiple genes are transcribed together, and e) Relatively compact genomes with little non-coding DNA.
For a eukaryotic genome, identify features such as: a) Exons and introns within genes, requiring detection of splice sites (donor and acceptor sites), b) Promoter regions including TATA boxes and other regulatory elements upstream of transcription start sites, c) Polyadenylation signals downstream of coding regions, d) Larger intergenic regions and repetitive sequences, and e) Presence of untranslated regions (UTRs) at the 5' and 3' ends of transcripts.
Use computational tools to scan the sequence for these hallmarks: for example, algorithms that detect ORFs, promoter motifs, splice sites, and conserved regulatory sequences. Comparative genomics can also help by identifying conserved sequences across related species.
Summarize that bacterial genomes are generally simpler with continuous coding sequences and clear promoter and ribosome binding sites, while eukaryotic genomes require more complex analysis due to introns, extensive regulatory regions, and larger non-coding DNA.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
56sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gene Structure and Regulatory Elements
Genes consist of coding regions (exons) and non-coding regions (introns in eukaryotes), along with regulatory sequences like promoters and enhancers. Identifying these features helps locate genes within a genome. In bacteria, genes are often organized in operons with promoters and terminators, while eukaryotic genes have more complex regulatory elements and splicing signals.
Recommended video:
Guided course
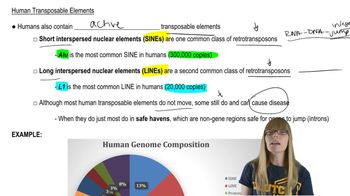
Human Transposable Elements
Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genomes
Bacterial genomes are typically compact, with densely packed genes, few introns, and operon structures. Eukaryotic genomes are larger, contain introns, repetitive sequences, and complex regulatory regions. Recognizing these differences is essential for accurate gene annotation in each genome type.
Recommended video:
Guided course
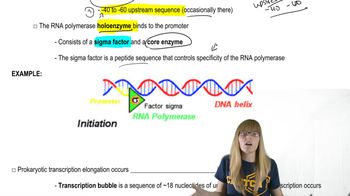
Prokaryotic Transcription
Sequence Features Indicative of Genes
Key sequence features include open reading frames (ORFs), start and stop codons, ribosome binding sites in bacteria, splice sites in eukaryotes, and conserved motifs. Detecting these features in unknown sequences aids in predicting gene locations and functions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sequencing Difficulties
Related Practice
Textbook Question
757
views
Textbook Question
Compare and contrast WGS to a map-based cloning approach.
632
views
Textbook Question
What is bioinformatics, and why is this discipline essential for studying genomes? Provide two examples of bioinformatics applications.
641
views
Textbook Question
How do high-throughput techniques such as computer-automated, next-generation sequencing, and mass spectrometry facilitate research in genomics and proteomics? Explain.
849
views
Textbook Question
BLAST searches and related applications are essential for analyzing gene and protein sequences. Define BLAST, describe basic features of this bioinformatics tool, and give an example of information provided by a BLAST search.
1047
views
Textbook Question
What functional information about a genome can be determined through applications of chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)?
673
views
