Students in a genetics laboratory began an experiment in an attempt to increase heat tolerance in two strains of Drosophila melanogaster. One strain was trapped from the wild six weeks before the experiment was to begin; the other was obtained from a Drosophila repository at a university laboratory. In which strain would you expect to see the most rapid and extensive response to heat-tolerance selection, and why?

Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
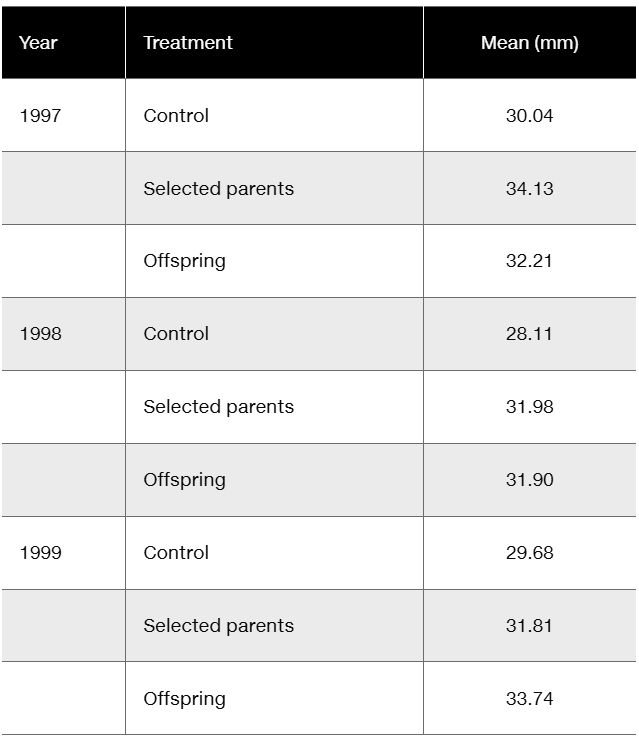
Considering that differences in control values represent year-to-year differences in greenhouse conditions, calculate (in mm) the average response to selection over the three-year period.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Heritability

Artificial Selection

Response to Selection

Consider a true-breeding plant, AABBCC, crossed with another true-breeding plant, aabbcc, whose resulting offspring are AaBbCc. If you cross the F₁ generation, and independent assortment is operational, the expected fraction of offspring in each phenotypic class is given by the expression N!/M!(N−M)! where N is the total number of alleles (six in this example) and M is the number of uppercase alleles. In a cross of AaBbCc×AaBbCc, what proportion of the offspring would be expected to contain two uppercase alleles?
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in a modified form and content.
Considering that differences in control values represent year-to-year differences in greenhouse conditions, calculate (in mm) the average response to selection over the three-year period
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
Calculate the realized heritability for each year and the overall realized heritability.
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
Assuming that the realized heritability in phlox is relatively high, what factors might account for such a high response?
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
In terms of evolutionary potential, is a population with high heritability likely to be favored compared to one with a low realized heritability?
