What possible conclusions can be drawn from the observations that in male Drosophila, no crossing over occurs, and that during meiosis, synaptonemal complexes are not seen in males but are observed in females where crossing over occurs?

An organism of the genotype AaBbCc was testcrossed to a triply recessive organism (aabbcc). The genotypes of the progeny are presented in the following table.
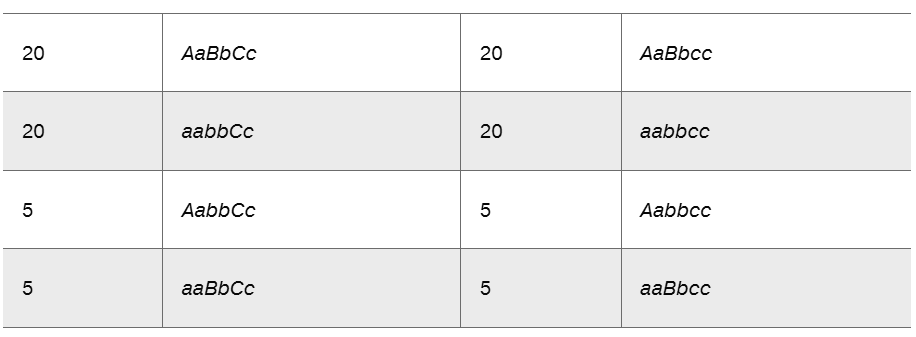
What can you conclude from the actual data about the location of the three genes in relation to one another?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Testcross and Its Purpose

Gene Linkage and Recombination

Interpreting Progeny Ratios to Map Genes

An organism of the genotype AaBbCc was testcrossed to a triply recessive organism (aabbcc). The genotypes of the progeny are presented in the following table.
If these three genes were all assorting independently, how many genotypic and phenotypic classes would result in the offspring, and in what proportion, assuming simple dominance and recessiveness in each gene pair?
An organism of the genotype AaBbCc was testcrossed to a triply recessive organism (aabbcc). The genotypes of the progeny are presented in the following table.
Answer part (a) again, assuming the three genes are so tightly linked on a single chromosome that no crossover gametes were recovered in the sample of offspring.
Based on our discussion of the potential inaccuracy of mapping, would you revise your answer to Problem 22? If so, how?
Traditional gene mapping has been applied successfully to a variety of organisms including yeast, fungi, maize, and Drosophila. However, human gene mapping has only recently shared a similar spotlight. What factors have delayed the application of traditional gene-mapping techniques in humans?
DNA markers have greatly enhanced the mapping of genes in humans. What are DNA markers, and what advantage do they confer?
