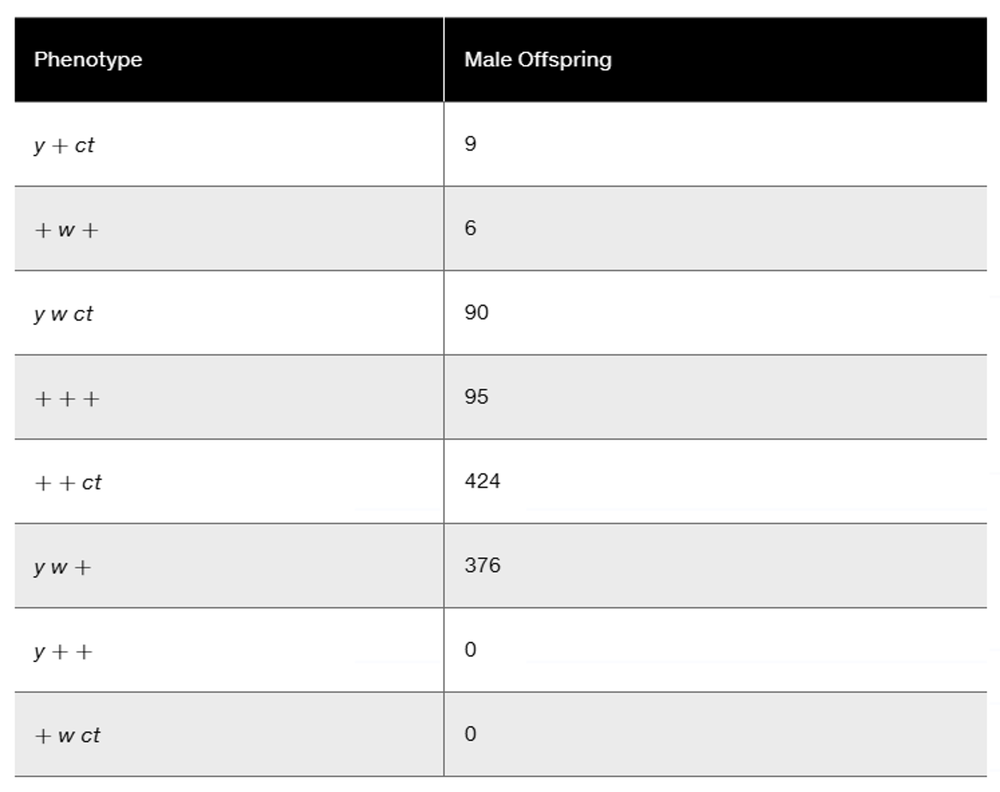
In Drosophila, a cross was made between females—all expressing the three X-linked recessive traits scute bristles (sc), sable body (s), and vermilion eyes (v)—and wild-type males. In the F1, all females were wild type, while all males expressed all three mutant traits. The cross was carried to the F2 generation, and 1000 offspring were counted, with the results shown in the following table.
No determination of sex was made in the data.
Determine the sequence of the three genes and the map distances between them.