In studies of recombination between mutants 1 and 2 from Problem 21, the results shown in the following table were obtained.
Calculate the recombination frequency.

 Klug 12th Edition
Klug 12th Edition Ch. 6 - Genetic Analysis and Mapping in Bacteria and Bacteriophages
Ch. 6 - Genetic Analysis and Mapping in Bacteria and Bacteriophages Problem 24a
Problem 24a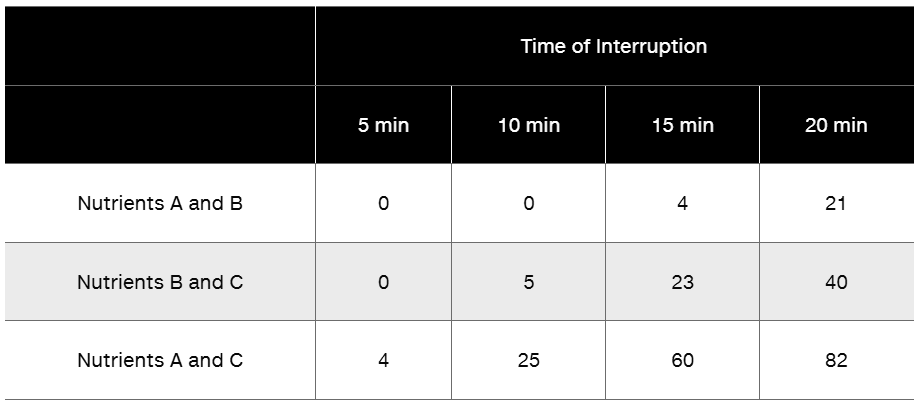
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


In studies of recombination between mutants 1 and 2 from Problem 21, the results shown in the following table were obtained.
Calculate the recombination frequency.
In studies of recombination between mutants 1 and 2 from Problem 21, the results shown in the following table were obtained.
When mutant 6 was tested for recombination with mutant 1, the data were the same as those shown above for strain B, but not for K12. The researcher lost the K12 data but remembered that recombination was ten times more frequent than when mutants 1 and 2 were tested. What were the lost values (dilution and plaque numbers)?
In Bacillus subtilis, linkage analysis of two mutant genes affecting the synthesis of two amino acids, tryptophan (trp₂⁻) and tyrosine (trp₁⁻), was performed using transformation. Examine the following data and draw all possible conclusions regarding linkage. What is the purpose of Part B of the experiment? [Reference: E. Nester, M. Schafer, and J. Lederberg (1963).]
An Hfr strain is used to map three genes in an interrupted mating experiment. The cross is Hfr/a⁺b⁺c⁺ rif x F⁻/a⁻b⁻c⁻ rifT (No map order is implied in the listing of the alleles; rifT is resistance to the antibiotic rifampicin.) The a⁺ gene is required for the biosynthesis of nutrient A, the b⁺ gene for nutrient B, and the c⁺ gene for nutrient C. The minus alleles are auxotrophs for these nutrients. The cross is initiated at time = 0, and at various times, the mating mixture is plated on three types of medium. Each plate contains minimal medium (MM) plus rifampicin plus specific supplements that are indicated in the following table. (The results for each time interval are shown as the number of colonies growing on each plate.)
Based on these data, determine the approximate location on the chromosome of the a, b, and c genes relative to one another and to the F factor.
An Hfr strain is used to map three genes in an interrupted mating experiment. The cross is Hfr/a⁺b⁺c⁺ rif x F⁻/a⁻b⁻c⁻ rifT (No map order is implied in the listing of the alleles; rifT is resistance to the antibiotic rifampicin.) The a⁺ gene is required for the biosynthesis of nutrient A, the b⁺ gene for nutrient B, and the c⁺ gene for nutrient C. The minus alleles are auxotrophs for these nutrients. The cross is initiated at time = 0, and at various times, the mating mixture is plated on three types of medium. Each plate contains minimal medium (MM) plus rifampicin plus specific supplements that are indicated in the following table. (The results for each time interval are shown as the number of colonies growing on each plate.)
Can the location of the rif gene be determined in this experiment? If not, design an experiment to determine the location of rif relative to the F factor and to gene b.
A plaque assay is performed beginning with 1 mL of a solution containing bacteriophages. This solution is serially diluted three times by combining 0.1 mL of each sequential dilution with 9.9 mL of liquid medium. Then 0.1 mL of the final dilution is plated in the plaque assay and yields 17 plaques. What is the initial density of bacteriophages in the original 1 mL?