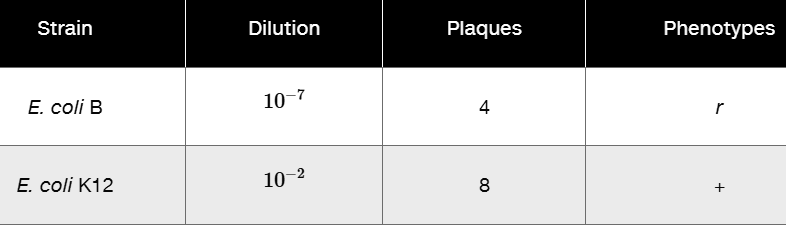
Using mutants 2 and 3 from Problem 19, following mixed infection on E. coli B, progeny viruses were plated in a series of dilutions on both E. coli B and K12 with the following results.
Another mutation, 6, was tested in relation to mutations 1 through 5 from Problems 18–20. In initial testing, mutant 6 complemented mutants 2 and 3. In recombination testing with 1, 4, and 5, mutant 6 yielded recombinants with 1 and 5, but not with 4. What can you conclude about mutation 6?