How is positional information provided along the anterior–posterior axis in Drosophila? What are the functions of bicoid and nanos?

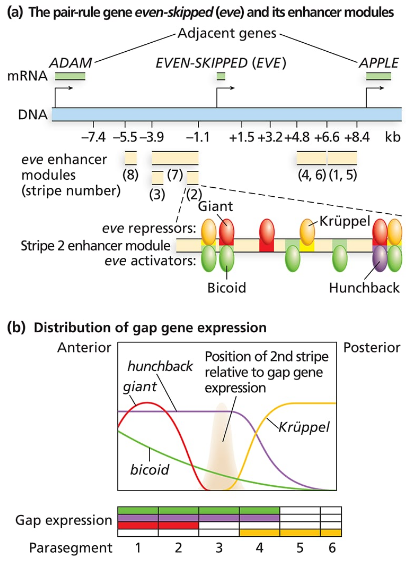
Consider the even-skipped regulatory sequences in the following figure:
How are the sharp boundaries of expression of Eve Stripe 2 formed?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Gene Regulatory Sequences

Transcription Factor Gradients and Combinatorial Control

Enhancer-Mediated Spatial Patterning

Early development in Drosophila is atypical in that pattern formation takes place in a syncytial blastoderm, allowing free diffusion of transcription factors between nuclei. In many other animal species, the fertilized egg is divided by cellular cleavages into a larger and larger number of smaller and smaller cells.
What constraints does the formation of a syncytial blastoderm impose on the mechanisms of pattern formation?
Early development in Drosophila is atypical in that pattern formation takes place in a syncytial blastoderm, allowing free diffusion of transcription factors between nuclei. In many other animal species, the fertilized egg is divided by cellular cleavages into a larger and larger number of smaller and smaller cells.
How must the model that describes Drosophila development be modified for describing animal species whose early development is not syncytial?
Consider the even-skipped regulatory sequences in Figure 18.9.
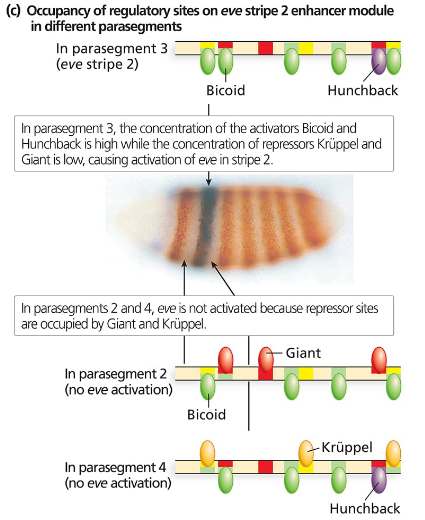
Consider the binding sites for gap proteins and Bicoid in the stripe 2 enhancer module. What sites are occupied in parasegments 2, 3, and 4, and how does this result in expression or no expression?
Consider the even-skipped regulatory sequences in Figure 18.9.
Explain what you expect to see happen to even-skipped stripe 2 if it is expressed in a Krüppel mutant background. What about a hunchback mutant background? A giant mutant background? A bicoid mutant background?
What is the difference between a parasegment and a segment in Drosophila development? Why do developmental biologists think of parasegments as the subdivisions that are produced during the development of flies?
