Cross-1 shown in the following figure illustrates genetic complementation of flower-color mutants. The produced from this cross of two pure-breeding mutant parental plants are dihybrid (CcPp) and have wild-type flower color. If these F₁ are allowed to self-fertilize, what phenotypes are expected in the F₂ , and what are the expected ratios of the phenotypes?

Epistatic gene interaction results in a modification of the F₂ dihybrid ratio.
What genetic principle is the basis of this expected F₂ ratio?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
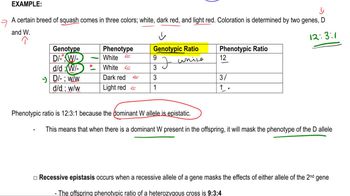
Epistasis
Dihybrid Cross
Mendelian Inheritance

The wild-type allele of a gene has an A–T base pair at a particular location in its sequence, and a mutant allele of the same gene has a G–C base pair at the same location. Otherwise, the sequences of the two alleles are identical. Does this information tell you anything about the dominance relationship of the alleles? Explain why or why not.
Epistatic gene interaction results in a modification of the F₂ dihybrid ratio.
What is the expected F₂ ratio?
Epistatic gene interaction results in a modification of the F₂ dihybrid ratio.
Give two examples of modified F₂ ratios produced by epistatic gene interactions and describe how gene interaction results in the ratios.
Draw a pedigree containing two parents and four children. Both of the parents have AB blood type. The first child is type A, the second child is type AB, and the third child is type B.
Assign the genotypes to these five people.
Draw a pedigree containing two parents and four children. Both of the parents have an AB blood type. The first child is type A, the second child is type AB, and the third child is type B.
The fourth child tests as having blood type O, which is not possible given the parental genotypes. Look at the Figure below and read the description of the molecular process that generates ABO blood group antigens. What other mutation could account for this observation?
