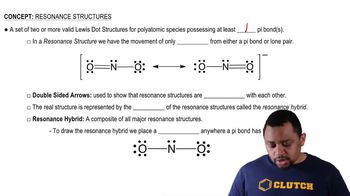
Step 3: Identify errors in the structure. In the provided structure, the nitrogen atom has 4 bonds, which exceeds its typical bonding capacity of 3. This violates the octet rule for nitrogen. Additionally, the oxygen atom appears correctly bonded but ensure its lone pairs are consistent with its valence electrons.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance