Textbook Question
What functional groups are found in all monosaccharides?
1531
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
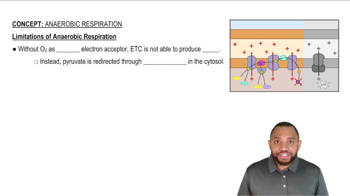
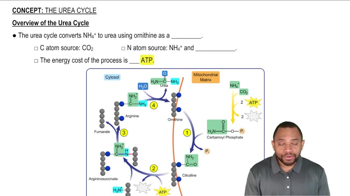
What functional groups are found in all monosaccharides?
What are the functional groups and number of carbons in a ketopentose?
Classify each of the following monosaccharides as an aldopentose, ketopentose, aldohexose, or ketohexose:
a. Psicose is present in low amounts in foods.