Textbook Question
Using the Chemistry Link to Health: Elements Essential to Health, answer each of the following:
b. What is the role of sulfur in the human body?
692
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Using the Chemistry Link to Health: Elements Essential to Health, answer each of the following:
b. What is the role of sulfur in the human body?
Using the Chemistry Link to Health: Elements Essential to Health, answer each of the following:
c. How many grams of sulfur would be a typical amount in a 60.-kg adult?
Using the Chemistry Link to Health: Elements Essential to Health, answer each of the following:
a. What is a micromineral?
Is each of the following statements true or false?
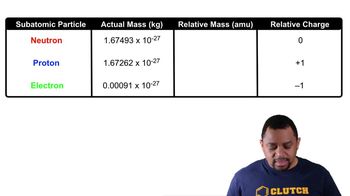
c. Neutrons repel each other.
On a dry day, your hair flies apart when you brush it. How would you explain this?
Sometimes clothes cling together when removed from a dryer. What kinds of charges are on the clothes?