Back
BackProblem 1
Discuss the usual mode of entry of bacteria into the skin. Compare bacterial skin infections with infections caused by fungi and viruses with respect to mode of entry.
Problem 2
What bacteria are identified by a positive coagulase test? What bacteria are characterized as group A beta-hemolytic?
Problem 3
On the following figure, show the sites of the following infections: impetigo, folliculitis, acne, warts, shingles, sporotrichosis, pediculosis.
<IMAGE>
Problem 4
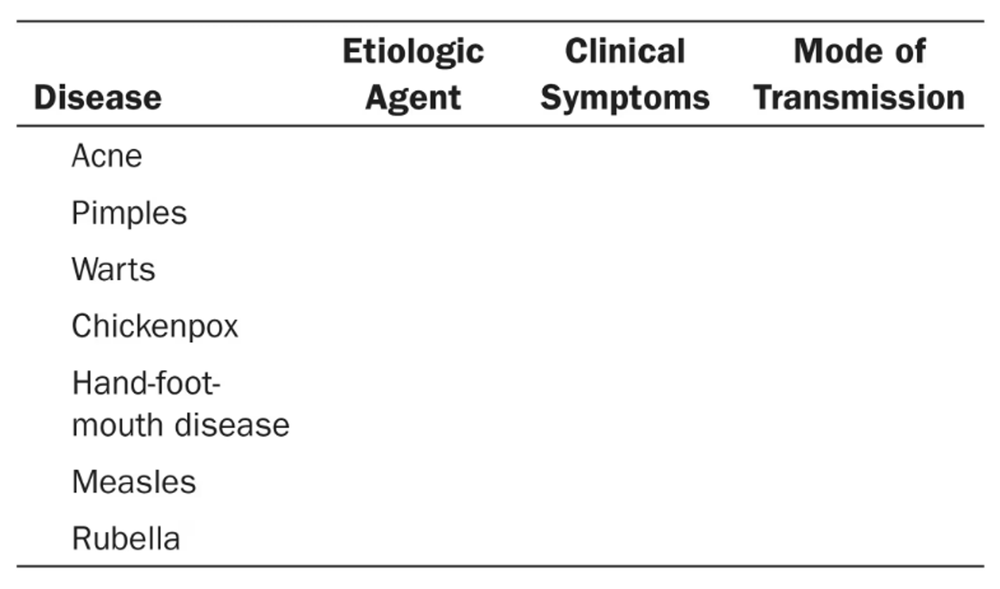
Complete the following table of epidemiology.
Problem 5
Before 2005, why was a test for antibodies against rubella required for females under age 50 before issuing a marriage license?
Problem 6
Identify the diseases based on the symptoms in the following chart.
Problem 7
What complications can occur from HSV-1 infections?
Problem 8
What is in the MMR vaccine?
Problem 9
A patient exhibits inflammatory skin lesions that itch intensely. Microscopic examination of skin scrapings reveals an eight-legged arthropod. What is your diagnosis? How is the disease treated? What would you conclude if you saw a six-legged arthropod?
Problem 10
This anaerobic, gram-positive rod is found on the skin. Infections are often treated with retinoids or benzoyl peroxide.
Problem 1
A 6-year old girl was taken to the physician for evaluation of a slowly growing bump on the back of her head. The bump was a raised, scaling lesion 4 cm in diameter. A fungal culture of material from the lesion was positive for a fungus with numerous conidia.
The girl’s disease was
a. Rubella.
b. Candidiasis.
c. Dermatomycosis.
d. A cold sore.
e. None of the above.
Problem 2
A 6-year old girl was taken to the physician for evaluation of a slowly growing bump on the back of her head. The bump was a raised, scaling lesion 4 cm in diameter. A fungal culture of material from the lesion was positive for a fungus with numerous conidia.
Besides the scalp, this disease can occur on all of the following except
a. Feet.
b. Nails.
c. The groin.
d. Subcutaneous tissue.
e. The disease can occur on all of these areas.
Problem 3
A 12-year old boy had a fever, rash, headache, sore throat, and cough. He also had a macular rash on his trunk, face, and arms. A throat culture was negative for Streptococcus pyogenes.
The boy most likely had
a. Streptococcal sore throat.
b. Measles.
c. Rubella.
d. Smallpox.
e. Hand-foot-mouth disease.
Problem 4
A 12-year old boy had a fever, rash, headache, sore throat, and cough. He also had a macular rash on his trunk, face, and arms. A throat culture was negative for Streptococcus pyogenes.
All of the following are complications of this disease except
a. Middle ear infections.
b. Pneumonia.
c. Birth defects.
d. Encephalitis.
e. All are complications of this disease.
Problem 5
A patient has conjunctivitis. If you isolated Pseudomonas from the patient’s mascara, you would most likely conclude all of the following except that
a. The mascara was the source of the infection.
b. Pseudomonas is causing the infection.
c. Pseudomonas has been growing in the mascara.
d. The mascara was contaminated by the manufacturer.
e. All of the above are valid conclusions.
Problem 6
You microscopically examine scrapings from a case of Acanthamoeba keratitis. You expect to see
a. Nothing.
b. Viruses.
c. Gram-positive cocci.
d. Eukaryotic cells.
e. Gram-negative cocci.
Problem 7
Use the following choices to answer the question given below.
a. Pseudomonas
b. Staphylococcus aureus
c. Scabies
d. Sporothrix
e. Virus
Nothing is seen in microscopic examination of a scraping from the patient’s rash.
Problem 8
Use the following choices to answer the question given below.
a. Pseudomonas
b. Staphylococcus aureus
c. Scabies
d. Sporothrix
e. Virus
Microscopic examination of the patient’s ulcer reveals 10μm ovoid cells.
Problem 9
Use the following choices to answer questions 8–10:
a. Apicomplexa
b. Ciliates
c. Dinoflagellates
d. Microsporidia
These are nonmotile parasites with special organelles for penetrating host tissue.
Problem 9a
Use the following choices to answer the question given below.
a. Pseudomonas
b. Staphylococcus aureus
c. Scabies
d. Sporothrix
e. Virus
Microscopic examination of scrapings from the patient’s rash shows gram-negative rods.
Problem 10
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a. Leading infectious cause of blindness—Chlamydia
b. Chickenpox—shingles
c. HSV-1—encephalitis
d. Buruli ulcer—stomach acid
e. None of the above