The angle θ through which a disk drive turns is given by θ(t) = a + bt - ct3, where a, b, and c are constants, t is in seconds, and θ is in radians. When t = 0, θ = π/4 rad and the angular velocity is 2.00 rad/s. When t = 1.50 s, the angular acceleration is 1.25 rad/s2. What are θ and the angular velocity when the angular acceleration is 3.50 rad/s2?

A wheel is rotating about an axis that is in the z-direction. The angular velocity ωz is -6.00 rad/s at t = 0, increases linearly with time, and is +4.00 rad/s at t = 7.00 s. We have taken counterclockwise rotation to be positive. What is the angular displacement of the wheel at t = 7.00 s?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
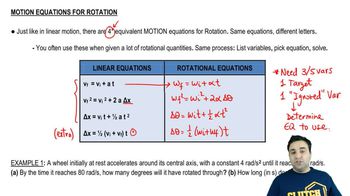
Angular Velocity

Angular Displacement

Kinematics of Rotational Motion
A wheel is rotating about an axis that is in the z-direction. The angular velocity ωz is -6.00 rad/s at t = 0, increases linearly with time, and is +4.00 rad/s at t = 7.00 s. We have taken counterclockwise rotation to be positive. Is the angular acceleration during this time interval positive or negative?
A wheel is rotating about an axis that is in the z-direction. The angular velocity ωz is -6.00 rad/s at t = 0, increases linearly with time, and is +4.00 rad/s at t = 7.00 s. We have taken counterclockwise rotation to be positive. During what time interval is the speed of the wheel increasing? Decreasing?
A bicycle wheel has an initial angular velocity of 1.50 rad/s. (a) If its angular acceleration is constant and equal to 0.200 rad/s2, what is its angular velocity at t = 2.50 s? (b) Through what angle has the wheel turned between t = 0 and t = 2.50 s?
An electric fan is turned off, and its angular velocity decreases uniformly from 500 rev/min to 200 rev/min in 4.00 s. Find the angular acceleration in rev/s2 and the number of revolutions made by the motor in the 4.00-s interval.
An electric fan is turned off, and its angular velocity decreases uniformly from 500 rev/min to 200 rev/min in 4.00 s. How many more seconds are required for the fan to come to rest if the angular acceleration remains constant at the value calculated in part (a)?
