Leukocytes are:
a. Nucleated cells that function in blood clotting
b. Nucleated cells that function in immunity
c. Anucleate cells that function in blood clotting
d. Anucleate cells that function in immunity

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
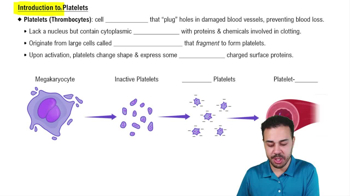

Leukocytes are:
a. Nucleated cells that function in blood clotting
b. Nucleated cells that function in immunity
c. Anucleate cells that function in blood clotting
d. Anucleate cells that function in immunity
Match the following leukocytes with the correct definition.
__Basophil
__B lymphocyte
__Neutrophil
__Monocyte
__T lymphocyte
__Eosinophil
a. Destroys bacteria; directly phagocytoses bacteria
b. Responds to parasitic worm infection and mediates the allergic response
c. Activates all parts of the immune response; directly kills cancer or virally infected cells
d. Secretes inflammatory mediators
e. Agranulocyte that matures into macrophage
f. Agranulocyte that secretes antibodies
Lymphocytes are derived from the _____ cell line, whereas the other leukocytes are derived from the _____ cell line.
Number the steps of hemostasis in order, putting 1 by the first event, 2 by the second, and so on.
____The intrinsic/contact activation and extrinsic/tissue factor pathways produce factor Xa.
____The clot retracts.
____Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin, and fibrin glues the plug together.
____Platelets are activated, and the platelet plug forms.
____Vasoconstriction and increased tissue pressure decrease blood flow through the vessel.
____Tissue plasminogen activator activates plasmin, which degrades fibrin.
____The common pathway produces thrombin.
How do the intrinsic/contact activation and extrinsic/tissue factor coagulation pathways differ? How are they similar?
What are the overall goals of the common pathway of coagulation?