Explain how the structure of each of the following joint types follows its function.
Cartilaginous joint

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


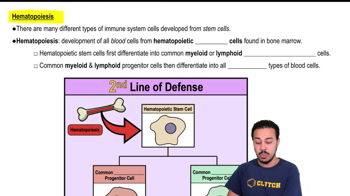
Explain how the structure of each of the following joint types follows its function.
Cartilaginous joint
When articular cartilage is damaged, often fibrocartilage forms instead of new hyaline cartilage. Does fibrocartilage have the same properties as hyaline cartilage? Is it likely to provide the same type of surface as hyaline cartilage? Explain. (Connects to Chapter 4)
Explain how the structure of each of the following joint types follows its function.
Synovial joint
Which functional joint class includes freely moveable joints?
a. Amphiarthroses
b. Synarthroses
c. Diarthroses
d. All functional joint classes are freely movable.
Identify each of the following joints as synovial, fibrous, or cartilaginous.
a. Pubic symphysis______
b. Elbow joint_____
c. Epiphyseal plate_______
d. Frontal suture_________
e. Gomphosis___________
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
Fibrous joints are united by collagen fibers.