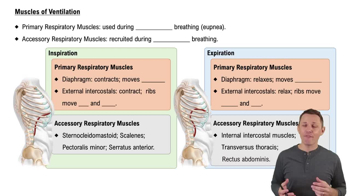
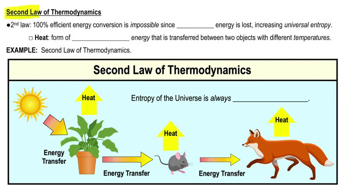
A baby holding its breath will:
a. Have brain cells damaged because of low blood oxygen levels
b. Automatically start to breathe again when the carbon dioxide levels in the blood reach a high enough value
c. Suffer heart damage because of increased pressure in the carotid sinus and aortic arch areas
d. Be called a 'blue baby'