Textbook Question
Which of the following would increase the rate of heat exchange between an animal and its environment?
a. Feathers or fur
b. Vasoconstriction
c. Wind blowing across the body surface
d. Countercurrent heat exchanger
1209
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
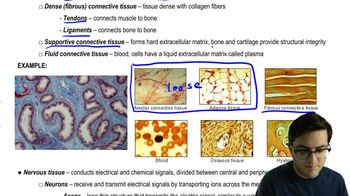


Which of the following would increase the rate of heat exchange between an animal and its environment?
a. Feathers or fur
b. Vasoconstriction
c. Wind blowing across the body surface
d. Countercurrent heat exchanger
Consider the energy budgets for a human, an elephant, a penguin, a mouse, and a snake. The would have the highest total annual energy expenditure, and the would have the highest energy expenditure per unit mass.
a. Elephant; mouse
b. Elephant; human
c. Mouse; snake
d. Penguin; mouse
Compared with a smaller cell, a larger cell of the same shape has
a. Less surface area
b. Less surface area per unit of volume
c. The same surface-area-to-volume ratio
d. A smaller cytoplasm-to-nucleus ratio