Activation of the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system
a. Increases heart rate
b. Enhances digestion
c. Triggers release of epinephrine
d. Causes conversion of glycogen to glucose

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Activation of the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system
a. Increases heart rate
b. Enhances digestion
c. Triggers release of epinephrine
d. Causes conversion of glycogen to glucose
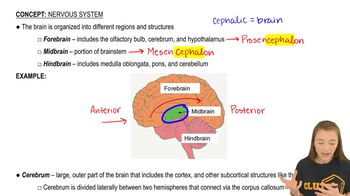
Which of the following structures or regions is incorrectly paired with its function?
a. Limbic system—motor control of speech
b. Medulla oblongata—homeostatic control
c. Cerebellum—coordination of movement and balance
d. Amygdala—emotional memory
Patients with damage to Wernicke's area have difficulty
a. Coordinating limb movement
b. Generating speech
c. Recognizing faces
d. Understanding language
After suffering a stroke, a patient can see objects anywhere in front of him but pays attention only to objects in his right field of vision. When asked to describe these objects, he has difficulty judging their size and distance. What part of the brain was likely damaged by the stroke?
a. The left frontal lobe
b. The right frontal lobe
c. The right parietal lobe
d. The corpus callosum
Injury localized to the hypothalamus would most likely disrupt
a. Regulation of body temperature
b. Short-term memory
c. Executive functions, such as decision making
d. Sorting of sensory information
The reflex that pulls your hand away when you prick your finger on a sharp object relies on a neuronal circuit with two synapses in the spinal cord. Using a circle to represent a cross-section of the spinal cord, draw the circuit. Label the types of neurons, the direction of information flow in each, and the locations of synapses.