Back
BackProblem 31
Distance to the Horizon The distance that a person can see to the horizon on a clear day from a point above the surface of Earth varies directly as the square root of the height at that point. If a person 144 m above the surface of Earth can see 18 km to the horizon, how far can a person see to the horizon from a point 64 m above the surface?
Problem 33
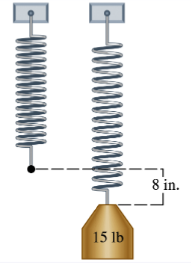
Hooke's Law for a Spring Hooke's law for an elastic spring states that the distance a spring stretches varies directly as the force applied. If a force of 15 lb stretches a certain spring 8 in., how much will a force of 30 lb stretch the spring?
Problem 35
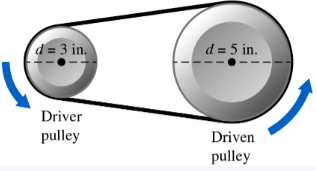
Solve each problem. The speed of a pulley varies inversely as its diameter. One kind of pulley, with diameter 3 in., turns at 150 revolutions per minute. Find the speed of a similar pulley with diameter 5 in.
Problem 37
Current Flow In electric current flow, it is found that the resistance offered by a fixed length of wire of a given material varies inversely as the square of the diameter of the wire. If a wire 0.01 in. in diameter has a resistance of 0.4 ohm, what is the resistance of a wire of the same length and material with diameter 0.03 in., to the nearest ten-thousandth of an ohm?
Problem 39
Simple Interest Simple interest varies jointly as principal and time. If $1000 invested for 2 yr earned $70, find the amount of interest earned by $5000 invested for 5 yr.
Problem 41
Force of Wind The force of the wind blowing on a vertical surface varies jointly as the area of the surface and the square of the velocity. If a wind of 40 mph exerts a force of 50 lb on a surface of 1/2 ft2, how much force will a wind of 80 mph place on a surface of 2 ft2?
Problem 45
Period of a Pendulum The period of a pendulum varies directly as the square root of the length of the pendulum and inversely as the square root of the acceleration due to gravity. Find the period when the length is 121 cm and the acceleration due to gravity is 980 cm per second squared, if the period is 6π seconds when the length is 289 cm and the acceleration due to gravity is 980 cm per second squared.
Problem 50
Nuclear Bomb Detonation Suppose the effects of detonating a nuclear bomb will be felt over a distance from the point of detonation that is directly proportional to the cube root of the yield of the bomb. Suppose a 100-kiloton bomb has certain effects to a radius of 3 km from the point of detonation. Find, to the nearest tenth, the distance over which the effects would be felt for a 1500-kiloton bomb.
Problem 54
What happens to y if y varies directly as x, and x is halved?
Problem 1
Provide a short answer to each question. What is the domain of the function ƒ(x)=1/x? What is its range?
Problem 3
Graph each quadratic function. Give the vertex, axis, x-intercepts, y-intercept, domain, range, and largest open intervals of the domain over which each function is increasing or decreasing. ƒ(x)=-3x2-12x-1
Problem 13
Use synthetic division to divide ƒ(x) by x-k for the given value of k. Then express ƒ(x) in the form ƒ(x)=(x-k)q(x)+r. ƒ(x)=5x3-3x2+2x-6; k=2
Problem 17
Use synthetic division to find ƒ(2). ƒ(x)=5x4-12x2+2x-8
Problem 18
Use synthetic division to find ƒ(2). ƒ(x)=x5+4x2-2x-4
Problem 21
If ƒ(x) is a polynomial function with real coefficients, and if 7+2i is a zero of the function, then what other complex number must also be a zero?
Problem 25
Find a polynomial function ƒ(x) of least degree with real coefficients having zeros as given. √3, -√3, 2, 3
Problem 26
Find a polynomial function ƒ(x) of least degree with real coefficients having zeros as given. -2+√5, -2-√5, -2, 1
Problem 30
Find all rational zeros of each function.
Problem 34
Solve each problem. Use Descartes' rule of signs to determine the different possibilities for the numbers of positive, negative, and nonreal complex zeros of .
Problem 35
Solve each problem. Is x+1 a factor of ƒ(x)=x3+2x2+3x+2?
Problem 37
Solve each problem. Find a polynomial function ƒ of degree 3 with -2, 1, and 4 as zeros, and ƒ(2)=16.
Problem 45
If the given term is the dominating term of a polynomial function, what can we conclude about each of the following features of the graph of the function? (a) domain (b) range (c) end behavior (d) number of zeros (e) number of turning points 10x7
Problem 46
If the given term is the dominating term of a polynomial function, what can we conclude about each of the following features of the graph of the function? (a) domain (b) range (c) end behavior (d) number of zeros (e) number of turning points -9x6
Problem 47
Graph each polynomial function. ƒ(x)=(x-2)2(x+3)
Problem 49
Graph each polynomial function. ƒ(x)=2x3+x2-x
Problem 52
Graph each polynomial function. ƒ(x)=-2x4+7x3-4x2-4x
Problem 53
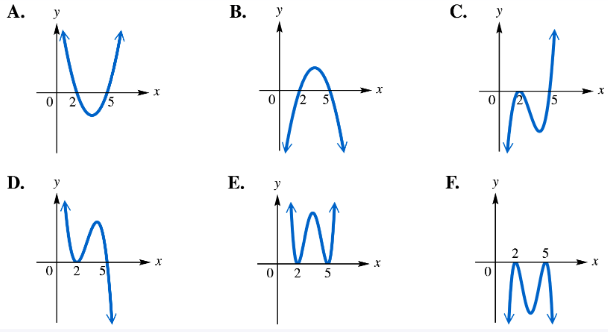
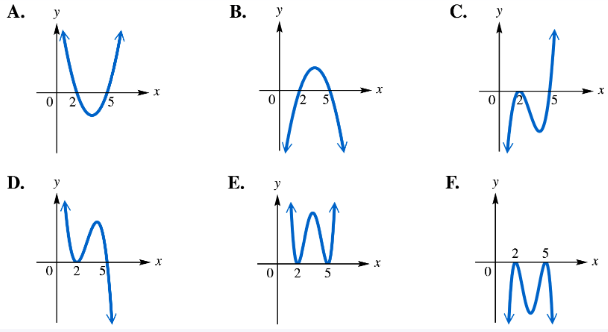
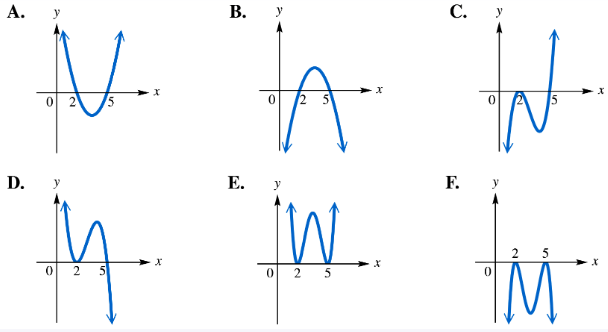
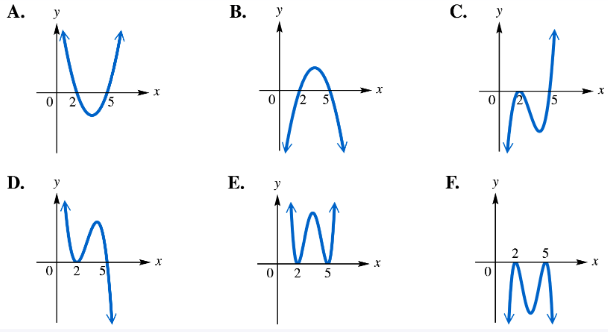
For each polynomial function, identify its graph from choices A–F. ƒ(x)=(x-2)2(x-5)
Problem 55
For each polynomial function, identify its graph from choices A–F. ƒ(x)=(x-2)2(x-5)2
Problem 57
For each polynomial function, identify its graph from choices A–F. ƒ(x)=-(x-2)(x-5)
Problem 58
For each polynomial function, identify its graph from choices A–F. ƒ(x)=-(x-2)2(x-5)2