Solve each problem. Suppose r varies directly as the square of m, and inversely as s. If r=12 when m=6 and s=4, find r when m=6 and s=20.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Rational Equations
Problem 33
Textbook Question
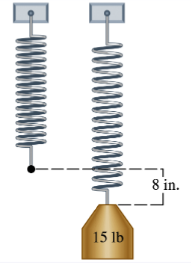
Hooke's Law for a Spring Hooke's law for an elastic spring states that the distance a spring stretches varies directly as the force applied. If a force of 15 lb stretches a certain spring 8 in., how much will a force of 30 lb stretch the spring?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the relationship given by Hooke's Law: the distance stretched \(d\) varies directly as the force applied \(F\). This can be written as \(d = kF\), where \(k\) is the constant of proportionality.
Use the given information to find the constant \(k\). Substitute \(F = 15\) lb and \(d = 8\) in. into the equation \(d = kF\) to get \$8 = k \times 15$.
Solve for \(k\) by dividing both sides of the equation by 15: \(k = \frac{8}{15}\).
Use the constant \(k\) to find the new distance stretched when the force is 30 lb. Substitute \(F = 30\) and \(k = \frac{8}{15}\) into \(d = kF\) to get \(d = \frac{8}{15} \times 30\).
Simplify the expression to find the distance \(d\) the spring stretches under a 30 lb force.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Direct Variation
Direct variation means one quantity changes proportionally with another. In this problem, the distance the spring stretches varies directly with the applied force, so if the force doubles, the stretch doubles. This relationship can be expressed as y = kx, where k is a constant.
Recommended video:

Maximum Turning Points of a Polynomial Function
Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law states that the force needed to stretch or compress a spring is proportional to the displacement from its rest position. Mathematically, F = kx, where F is force, x is displacement, and k is the spring constant. This law applies within the elastic limit of the spring.
Solving Proportions
Solving proportions involves setting two ratios equal to each other to find an unknown value. Here, the ratio of force to stretch length is constant, so you can set up the proportion 15/8 = 30/x and solve for x to find the new stretch length.
Recommended video:

Solving Logarithmic Equations

 5:56m
5:56mWatch next
Master Introduction to Rational Equations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
504
views
