Textbook Question
Write a chemical equation that illustrates the autoionization of water.
572
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
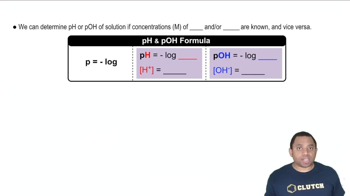


Write a chemical equation that illustrates the autoionization of water.
Write the expression for the ion product constant for water, Kw.
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) 3H+4 = 0.0505 M
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (b) 3H+4 = 2.5 * 10-10 M
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (c) a solution in which 3H+4 is 1000 times greater than 3OH-4.