For each of the following elements, write its chemical symbol, determine the name of the group to which it belongs (Table 2.3), and indicate whether it is a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal: (a) polonium (b) strontium (c) neon (d) rubidium (e) sulfur.
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 45b
The structural formulas of the compounds n-butane and isobutane are shown below. (b) Determine the empirical formula of each.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the molecular formula of isopentane by counting the number of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms in the structure.
Identify the molecular formula of hexane by counting the number of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms in the structure.
Determine the empirical formula of isopentane by finding the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in its molecular formula.
Determine the empirical formula of hexane by finding the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in its molecular formula.
Compare the empirical formulas of isopentane and hexane to see if they are the same or different.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Empirical Formula
The empirical formula of a compound represents the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements present in that compound. It is derived from the molecular formula by dividing the subscripts of each element by their greatest common divisor. For example, the empirical formula for C6H12 is CH2, indicating that for every carbon atom, there are two hydrogen atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Empirical vs Molecular Formula
Structural Formulas
Structural formulas depict the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, showing how the atoms are bonded to each other. They provide insight into the molecular geometry and can help identify isomers, which are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. Understanding structural formulas is crucial for determining the empirical formula accurately.
Recommended video:
Guided course
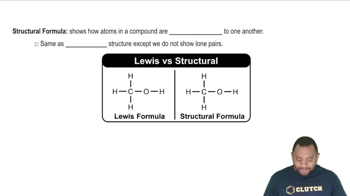
Structural Formula
Isomers
Isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms, leading to different properties. For instance, n-butane and isobutane are structural isomers, meaning they have the same molecular formula (C4H10) but different structural formulas. Recognizing isomers is essential when calculating empirical formulas, as it affects the interpretation of the molecular structure.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isomers
Related Practice
Textbook Question
603
views
Textbook Question
The structural formulas of the compounds n-butane and isobutane are shown below. (c) Which formulas—empirical, molecular, or structural—allow you determine these are different compounds?
604
views
Textbook Question
Ball-and-stick representations of benzene, a colorless liquid often used in organic chemistry reactions, and acetylene, a gas used as a fuel for high-temperature welding, are shown below. (a) Determine the molecular formula of each.
427
views
Textbook Question
What are the molecular and empirical formulas for each of the following compounds? Write the molecular formula for the following compound.
531
views
