Textbook Question
Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is a very soluble salt in water.(a) Draw the Lewis structures of the ammonium and chlorideions.
1145
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

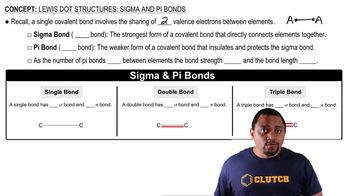

Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is a very soluble salt in water. (c) If you dissolve 14 g of ammonium chloride in 500.0 mL of water, what is the molar concentration of the solution?
Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is a very soluble salt in water. (d) How many grams of silver nitrate do you need to add to the solution in part (c) to precipitate all of the chloride as silver chloride?