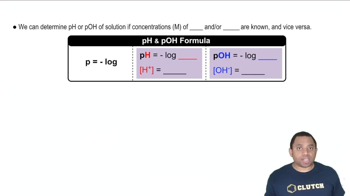
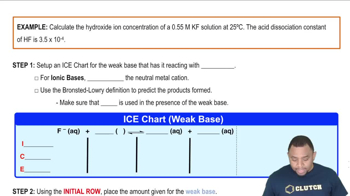
Base Dissociation Constant (Kb)
The base dissociation constant (Kb) quantifies the strength of a base in solution. It is defined as the equilibrium constant for the reaction in which a base accepts a proton from water, forming its conjugate acid and hydroxide ions. A higher Kb value indicates a stronger base, while a lower value suggests a weaker base. In this case, ammonia has a Kb of 1.8 x 10^-5, indicating it is a weak base.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance