Textbook Question
How do we know that chromosomes exist in homologous pairs?
495
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
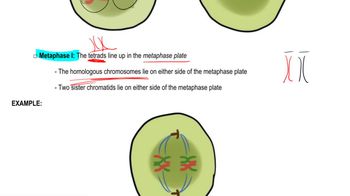


How do we know that chromosomes exist in homologous pairs?
How do we know that DNA replication occurs during interphase, not early in mitosis?
How do we know that mitotic chromosomes are derived from chromatin?
What role do the following cellular components play in the storage, expression, or transmission of genetic information?
(a) Chromatin
(b) Nucleolus
(c) Ribosome
(d) Mitochondrion
(e) Centriole
(f) Centromere
Discuss the concepts of homologous chromosomes, diploidy, and haploidy. What characteristics do two homologous chromosomes share?
If two chromosomes of a species are the same length and have similar centromere placements and yet are not homologous, what is different about them?