Textbook Question
How do we know that chromosomes exist in homologous pairs?
495
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

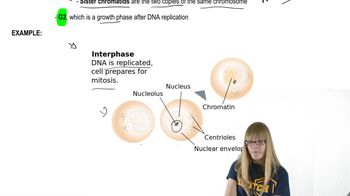

How do we know that chromosomes exist in homologous pairs?
How do we know that mitotic chromosomes are derived from chromatin?
Write a short essay that contrasts mitosis and meiosis, including their respective roles in organisms, the mechanisms by which they achieve their respective outcomes, and the consequences should either process fail to be executed with absolute fidelity.
What role do the following cellular components play in the storage, expression, or transmission of genetic information?
(a) Chromatin
(b) Nucleolus
(c) Ribosome
(d) Mitochondrion
(e) Centriole
(f) Centromere