Textbook Question
Write a short essay that distinguishes between the terms replication and synthesis, as applied to DNA. Which of the two is most closely allied with the field of biochemistry?
715
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


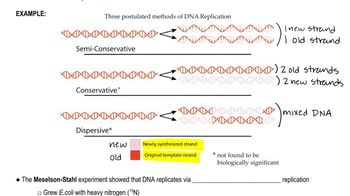
Write a short essay that distinguishes between the terms replication and synthesis, as applied to DNA. Which of the two is most closely allied with the field of biochemistry?
Compare conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive modes of DNA replication.
Describe the role of ¹⁵N in the Meselson–Stahl experiment.
What are the requirements for in vitro synthesis of DNA under the direction of DNA polymerase I?
In Kornberg's initial experiments, it was rumored that he grew E. coli in Anheuser-Busch beer vats. (Kornberg was working at Washington University in St. Louis.) Why do you think this might have been helpful to the experiment?
How did Kornberg assess the fidelity of DNA polymerase I in copying a DNA template?