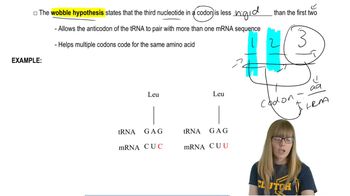
It has been suggested that the present-day triplet genetic code evolved from a doublet code when there were fewer amino acids available for primitive protein synthesis.
The amino acids Ala, Val, Gly, Asp, and Glu are all early members of biosynthetic pathways and are more evolutionarily conserved than other amino acids. They therefore probably represent 'early' amino acids. Of what significance is this information in terms of the evolution of the genetic code? Also, which base, of the first two within a coding triplet, would likely have been the more significant in originally specifying these amino acids?