Textbook Question
How do we know that the orientation of promoters relative to the transcription start site is important while enhancers are orientation independent?
612
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


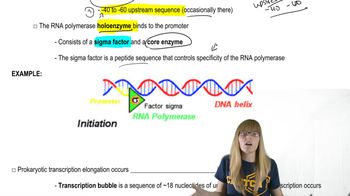
How do we know that the orientation of promoters relative to the transcription start site is important while enhancers are orientation independent?
How do we know that eukaryotic transcription factors bind to DNA sequences at or near promoter regions?
How do we know that there is an association between disease susceptibility in humans and regulatory DNA sequences?