The following variances were calculated for two traits in a herd of hogs.
Calculate broad-sense (H²) and narrow-sense (h²) heritabilities for each trait in this herd.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



The following variances were calculated for two traits in a herd of hogs.
Calculate broad-sense (H²) and narrow-sense (h²) heritabilities for each trait in this herd.
The following variances were calculated for two traits in a herd of hogs.
Which of the two traits will respond best to selection by a breeder? Why?
The mean and variance of plant height of two highly inbred strains (P₁ and P₂) and their progeny (F₁ and F₂) are shown here.
Strain Mean (cm) Variance
P₁ 34.2 4.2
P₂ 55.3 3.8
F₁ 44.2 5.6
F₂ 46.3 10.3
Calculate the broad-sense heritability (H²) of plant height in this species.
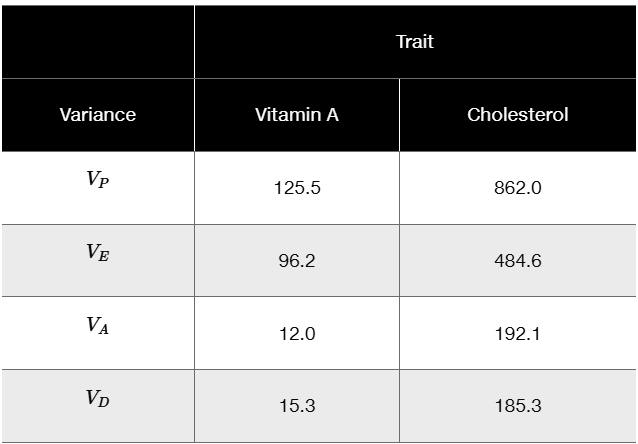
A hypothetical study investigated the vitamin A content and the cholesterol content of eggs from a large population of chickens. The following variances (V) were calculated.
Which trait, if either, is likely to respond to selection?
In a herd of dairy cows the narrow-sense heritability for milk protein content is 0.76, and for milk butterfat it is 0.82. The correlation coefficient between milk protein content and butterfat is 0.91. If the farmer selects for cows producing more butterfat in their milk, what will be the most likely effect on milk protein content in the next generation?
In an assessment of learning in Drosophila, flies were trained to avoid certain olfactory cues. In one population, a mean of 8.5 trials was required. A subgroup of this parental population that was trained most quickly (mean=6.0) was interbred, and their progeny were examined. These flies demonstrated a mean training value of 7.5. Calculate realized heritability for olfactory learning in Drosophila.