Textbook Question
There are four amine isomers with the molecular formula C3H9N. Draw their condensed structural formulas, write the common name, and classify each as a primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) amine.
838
views

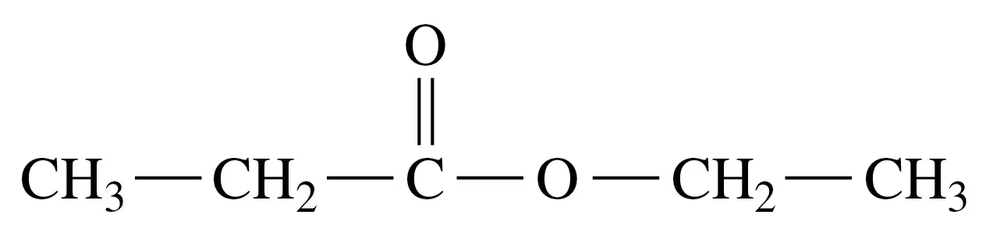
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


There are four amine isomers with the molecular formula C3H9N. Draw their condensed structural formulas, write the common name, and classify each as a primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) amine.
There are four amide isomers with the molecular formula C3H7NO. Draw their condensed structural formulas and write the IUPAC name for each.
Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, for each of the following:
a.
Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, for each of the following:
c.
Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, for each of the following:
e.
Draw the condensed structural formulas for a and b and line-angle formulas for c and d:
c. 3-bromopentanoic acid