Textbook Question
Predict the shape and polarity of each of the following molecules, which have polar covalent bonds:
a. A central atom with three identical bonded atoms and one lone pair.
1580
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Predict the shape and polarity of each of the following molecules, which have polar covalent bonds:
a. A central atom with three identical bonded atoms and one lone pair.
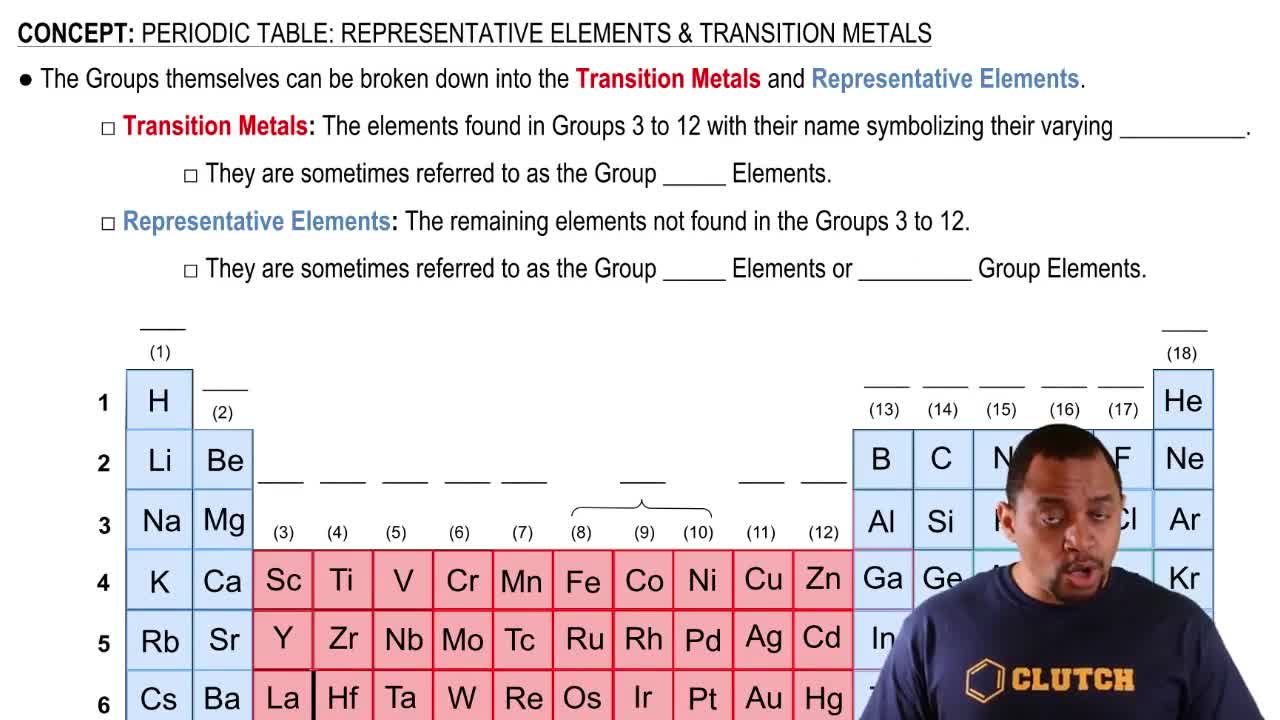
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
a. XCl3
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
b. Al2X3
Classify each of the following as ionic or molecular, and name each:
a. Li2HPO4
Classify each of the following as ionic or molecular, and name each:
b. Cl2O7
Complete the Lewis structure for each of the following:
a.