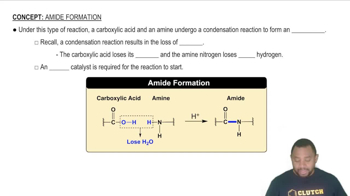
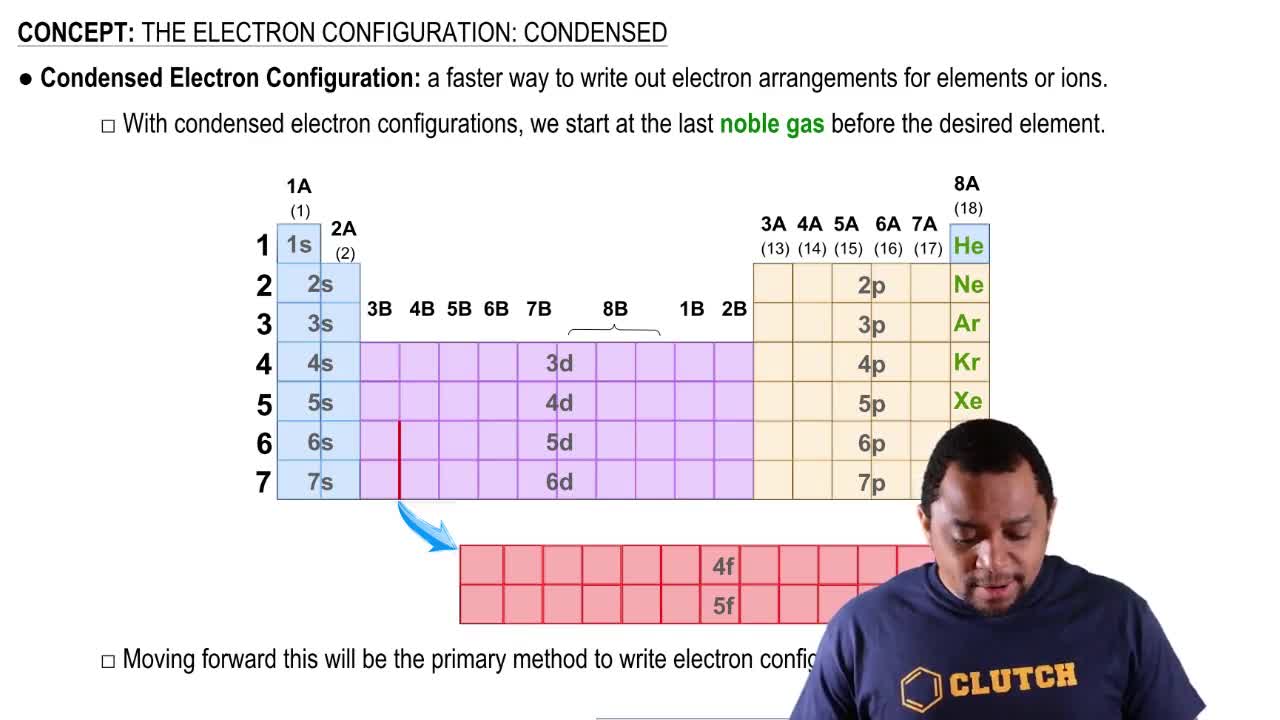
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals. For rubidium, the electron configuration is [Kr] 5s¹, indicating it has one electron in its outermost shell. When rubidium forms an ion, it loses this single valence electron, resulting in a stable electron configuration similar to that of krypton, which is essential for understanding its ionic behavior.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance