Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula if cyclic, for each of the following:
d. N-propylaniline
723
views

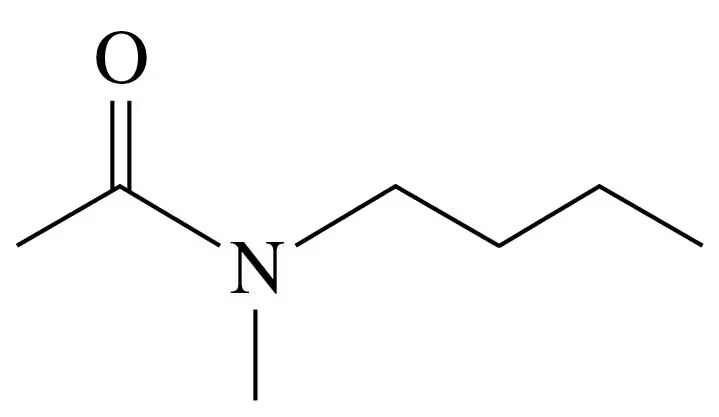
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula if cyclic, for each of the following:
d. N-propylaniline
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula if cyclic, for each of the following:
d. ethylmethylammonium bromide
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products of the following:
a. CH3–CH2–NH2 + H2O ⇌
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
a.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
b.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
b.