Textbook Question
Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following:
b. ethylcyclopentane
1596
views

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Problem 20c
Problem 20c Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

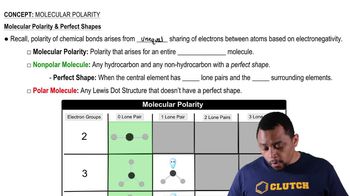
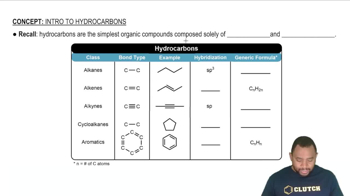
Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following:
b. ethylcyclopentane
Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following:
d. 2,3-dichlorohexane
Heptane, used as a solvent for rubber cement, has a density of 0.68 g/mL and boils at 98 °C.
d. Will heptane float on water or sink?
Write the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of each of the following compounds:
b. cyclopropane
Write the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of each of the following compounds:
c. 2,3-dimethylhexane
Identify the following as alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkenes, or alkynes:
a.