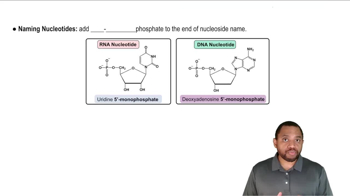
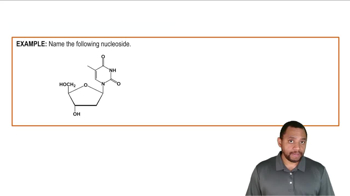
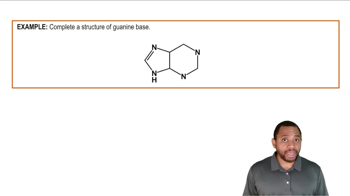
Suppose a mutation occurs in the DNA section in problem 17.89, and the first base in the parent chain, adenine, is replaced by guanine.
c. Write the three-letter symbols for the amino acids that would go into the peptide from the mRNA you wrote in part b.