Suppose a mutation occurs in the DNA section in problem 17.89, and the first base in the parent chain, adenine, is replaced by guanine.
b. Using the new strand that results from this mutation, write the order of bases in the altered mRNA.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Suppose a mutation occurs in the DNA section in problem 17.89, and the first base in the parent chain, adenine, is replaced by guanine.
b. Using the new strand that results from this mutation, write the order of bases in the altered mRNA.
Suppose a mutation occurs in the DNA section in problem 17.89, and the first base in the parent chain, adenine, is replaced by guanine.
c. Write the three-letter symbols for the amino acids that would go into the peptide from the mRNA you wrote in part b.
Suppose a mutation occurs in the DNA section in problem 17.89, and the first base in the parent chain, adenine, is replaced by guanine.
d. What effect, if any, might this mutation have on the structure and/or function of the resulting protein?
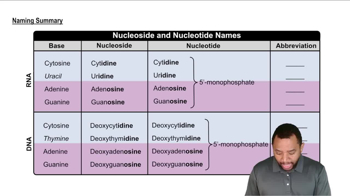
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleosides:
a. deoxythymidine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleosides:
c. cytidine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
b. dAMP