Textbook Question
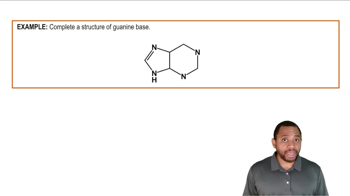
Identify each of the following bases as a pyrimidine or a purine:
a. cytosine
608
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Identify each of the following bases as a pyrimidine or a purine:
a. cytosine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleosides:
a. deoxythymidine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleosides:
c. cytidine
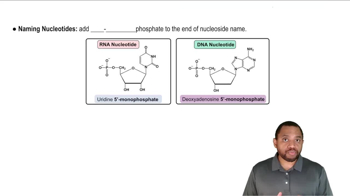
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
d. UMP
How do the bases cytosine and uracil differ?
Draw the condensed structural formula for CMP.