Textbook Question
Identify each of the following as catabolic or anabolic:
a. synthesis of lipids from glycerol and fatty acids
691
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
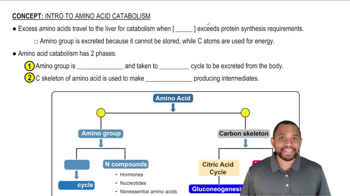


Identify each of the following as catabolic or anabolic:
a. synthesis of lipids from glycerol and fatty acids
Identify each of the following as catabolic or anabolic:
a. digestion of fats to fatty acids and glycerol
Identify each of the following as catabolic or anabolic:
c. synthesis of nucleic acids from nucleotides
What is the purpose of digestion in stage 1?