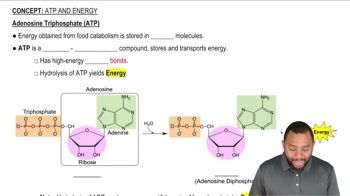
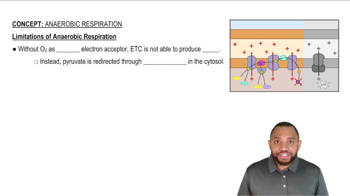
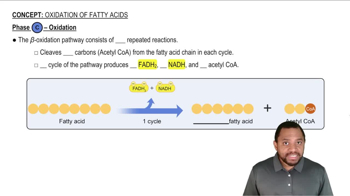
Identify each of the following reactions a to e in the β oxidation of palmitic acid, a C16 fatty acid, as
(1) activation
(2) first oxidation
(3) hydration
(4) second oxidation
(5) cleavage
a. Palmitoyl CoA and FAD form α, β-unsaturated palmitoyl CoA and FADH2.