Textbook Question
State whether each of the following refers to a saturated or an unsaturated solution:
a. A crystal added to a solution does not change in size.
1486
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


State whether each of the following refers to a saturated or an unsaturated solution:
a. A crystal added to a solution does not change in size.
State whether each of the following refers to a saturated or an unsaturated solution:
c. A uric acid concentration of 4.6 mg/100 mL in the kidney does not cause gout.
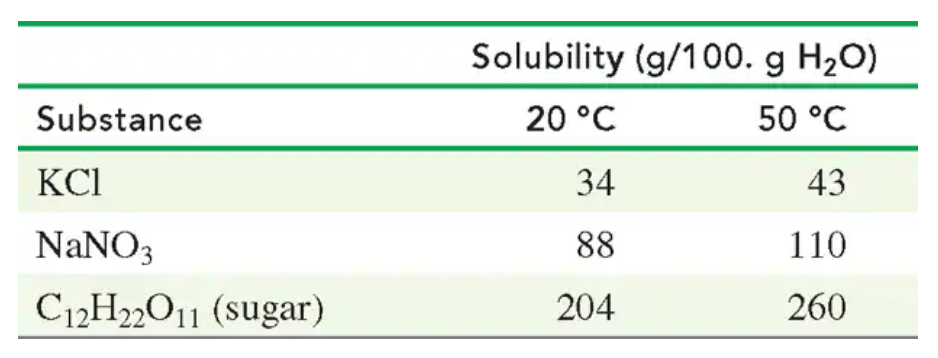
Use the following table:
A solution containing 80. g of KCl in 200. g of H2O at 50 °C is cooled to 20 °C.
a. How many grams of KCl remain in solution at 20 °C?
Explain the following observations:
a. More sugar dissolves in hot tea than in iced tea.
Predict whether each of the following ionic compounds is soluble in water:
c. BaCO3
Predict whether each of the following ionic compounds is soluble in water:
d. K2O