Diagram the roles that T cells and B cells play in immunity.
Ch. 17 - Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host

Tortora14th EditionMicrobiology: An IntroductionISBN: 9780138200398Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 6
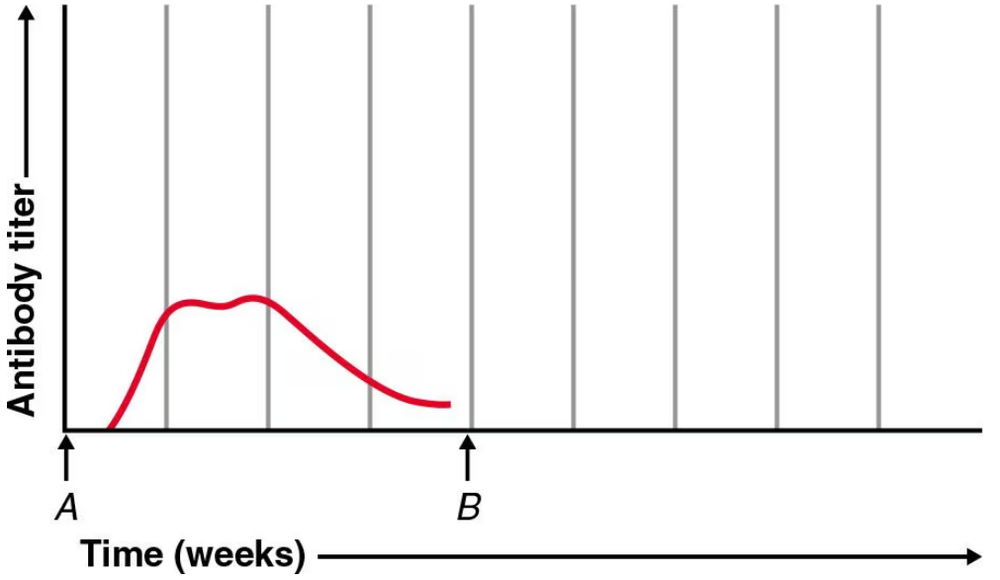
a. In the following graph, at time A the host was injected with tetanus toxoid. Show the response to a booster dose at time B.
b. Draw the antibody response of this same individual to exposure to a new antigen at time B.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the context of the problem. The host is first injected with tetanus toxoid at time A, which will initiate a primary immune response. This involves activation of naive B cells, production of IgM antibodies initially, followed by class switching to IgG antibodies, and formation of memory B cells.
Step 2: For part (a), consider what happens at time B when a booster dose of the same antigen (tetanus toxoid) is given. The immune system will mount a secondary (anamnestic) response. This response is faster, stronger, and predominantly involves IgG antibodies due to the presence of memory B cells formed during the primary response.
Step 3: To draw the antibody response for part (a), start with a smaller, slower rise in antibody levels after time A (primary response), then at time B, show a rapid and higher increase in antibody levels representing the secondary response. The curve after time B should peak higher and faster than after time A.
Step 4: For part (b), the individual is exposed to a new antigen at time B. Since this is a new antigen, the immune system will mount a primary response similar to the initial injection at time A. This means a slower rise in antibody levels, starting with IgM and then IgG, with no memory cells to speed up the response.
Step 5: To draw the antibody response for part (b), show a slow and gradual increase in antibody levels starting at time B, similar in shape and timing to the primary response seen at time A, but independent of the previous tetanus toxoid response.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
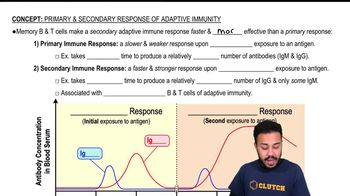
Primary and Secondary Immune Responses
The primary immune response occurs when the immune system first encounters an antigen, producing antibodies slowly and at lower levels. The secondary (or booster) response happens upon re-exposure to the same antigen, leading to a faster and stronger antibody production due to memory B cells formed during the primary response.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Primary and Secondary Response of Adaptive Immunity
Tetanus Toxoid and Vaccination
Tetanus toxoid is an inactivated toxin used as a vaccine to stimulate immunity without causing disease. It primes the immune system to recognize tetanus toxin, enabling a rapid and enhanced antibody response upon subsequent booster doses or exposure to the actual toxin.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Exotoxins vs. Endotoxin Review
Antibody Response to New Antigens
When the immune system encounters a new antigen for the first time, it mounts a primary response characterized by a lag phase before antibody production begins. This response is slower and produces fewer antibodies compared to a secondary response, as memory cells specific to the new antigen have not yet been formed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Outcomes of Antibody Binding to Antigen
Related Practice
Textbook Question
858
views
Textbook Question
Explain a function for the following types of cells: CTL, TH, and Treg. What is a cytokine?
1015
views
Textbook Question
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
Antibodies that protect the fetus and newborn.
810
views
Textbook Question
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
The first antibodies synthesized; especially effective against microorganisms.
651
views
Textbook Question
How would each of the following prevent infection?
a. Antibodies against Neisseria gonorrhoeae fimbriae
b. Antibodies against host cell mannose
670
views
Textbook Question
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
Antibodies that are bound to mast cells and involved in allergic reactions.
751
views
