A speed skater moving to the left across frictionless ice at 8.0 m/s hits a 5.0-m-wide patch of rough ice. She slows steadily, then continues on at 6.0 m/s. What is her acceleration on the rough ice?

Write a short description of the motion of a real object for which FIGURE EX1.20 would be a realistic position-versus-time graph.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Position vs. Time Graphs
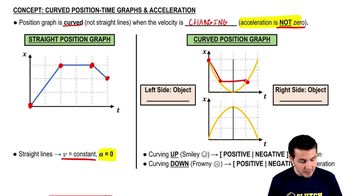
Types of Motion

Velocity and Acceleration

A Porsche challenges a Honda to a 400 m race. Because the Porsche's acceleration of 3.5 m/s2 is larger than the Honda's 3.0 m/s2, the Honda gets a 1.0 s head start. Who wins? By how many seconds?
FIGURE EX1.18 shows the motion diagram of a drag racer. The camera took one frame every 2 s. Make a position-versus-time graph for the drag racer. Because you have data only at certain instants, your graph should consist of dots that are not connected together.
Ball bearings are made by letting spherical drops of molten metal fall inside a tall tower—called a shot tower—and solidify as they fall. If a bearing needs 4.0 s to solidify enough for impact, how high must the tower be?
Ball bearings are made by letting spherical drops of molten metal fall inside a tall tower—called a shot tower—and solidify as they fall. What is the bearing's impact velocity?
A rock is tossed straight up from ground level with a speed of 20 m/s. When it returns, it falls into a hole 10 m deep. What is the rock's speed as it hits the bottom of the hole?
