A kayaker needs to paddle north across a 100-m-wide harbor. The tide is going out, creating a tidal current that flows to the east at 2.0 m/s. The kayaker can paddle with a speed of 3.0 m/s. How long will it take him to cross?

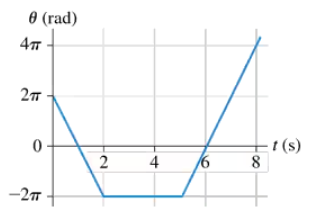
FIGURE EX4.24 shows the angular-position-versus-time graph for a particle moving in a circle. What is the particle's angular velocity at t = 4s
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Angular Position

Angular Velocity

Graph Interpretation
Susan, driving north at 60 mph, and Trent, driving east at 45 mph, are approaching an intersection. What is Trent's speed relative to Susan's reference frame?
FIGURE EX4.23 shows the angular-velocity-versus-time graph for a particle moving in a circle. How many revolutions does the object make during the first 4 s?
The earth's radius is about 4000 miles. Kampala, the capital of Uganda, and Singapore are both nearly on the equator. The distance between them is 5000 miles. The flight from Kampala to Singapore takes 9.0 hours. What is the plane's angular velocity with respect to the earth's surface? Give your answer in °/h.
As the earth rotates, what is the speed of a physics student in Miami, Florida, at latitude 26°. Ignore the revolution of the earth around the sun. The radius of the earth is 6400 km.
Peregrine falcons are known for their maneuvering ability. In a tight circular turn, a falcon can attain a centripetal acceleration 1.5 times the free-fall acceleration. What is the radius of the turn if the falcon is flying at 25 m/s?
