14 g of nitrogen gas at STP are adiabatically compressed to a pressure of 20 atm. What is the compression ratio Vmax/Vmin?

 Knight Calc 5th Edition
Knight Calc 5th Edition Ch 19: Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics
Ch 19: Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Problem 67a
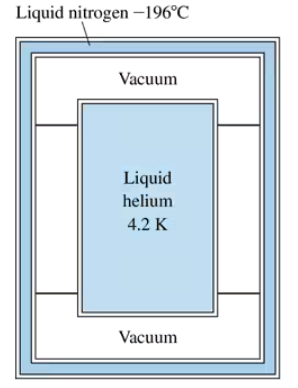
Problem 67aLiquid helium, with a boiling point of 4.2 K, is used in ultralow-temperature experiments and also for cooling the superconducting magnets used in MRI imaging in medicine. Storing liquid helium so far below room temperature is a challenge because even a small 'heat leak' will boil the helium away. A standard helium dewar, shown in FIGURE P19.67, has an inner stainless-steel cylinder filled with liquid helium surrounded by an outer cylindrical shell filled with liquid nitrogen at –196°C. The space between is a vacuum. The small structural supports have very low thermal conductivity, so you can assume that radiation is the only heat transfer between the helium and its surroundings. Suppose the helium cylinder is 16 cm in diameter and 30 cm tall and that all walls have an emissivity of 0.25. The density of liquid helium is 125 kg/m3 and its heat of vaporization is 2.1×104 J/kg. What is the mass of helium in the filled cylinder?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Density and Volume

Heat Transfer and Emissivity

Heat of Vaporization

14 g of nitrogen gas at STP are pressurized in an isochoric process to a pressure of 20 atm. What are the final temperature?
A monatomic gas is adiabatically compressed to 1/8 of its initial volume. Does each of the following quantities change? If so, does it increase or decrease, and by what factor? If not, why not? The molar specific heat at constant volume.
Most stars are main-sequence stars, a group of stars for which size, mass, surface temperature, and radiated power are closely related. The sun, for instance, is a yellow main-sequence star with a surface temperature of 5800 K. For a main-sequence star whose mass M is more than twice that of the sun, the total radiated power, relative to the sun, is approximately P/Psun=1.5(M/Msun)3.5. The star Regulus A is a bluish main-sequence star with mass 3.8Msun and radius 3.1Rsun. What is the surface temperature of Regulus A?
One cylinder in the diesel engine of a truck has an initial volume of 600 cm3. Air is admitted to the cylinder at 30°C and a pressure of 1.0 atm. The piston rod then does 400 J of work to rapidly compress the air. What are its final temperature and volume?
A flow-through electric water heater has a 20 kW electric heater inside an insulated 2.0-cm-diameter pipe so that water flowing through the pipe will have good thermal contact with the heater. Assume that all the heat energy is transferred to the water. Suppose the inlet water temperature is 12°C and the flow rate is 8.0 L/min (about that of a standard shower head). What is the outlet temperature?